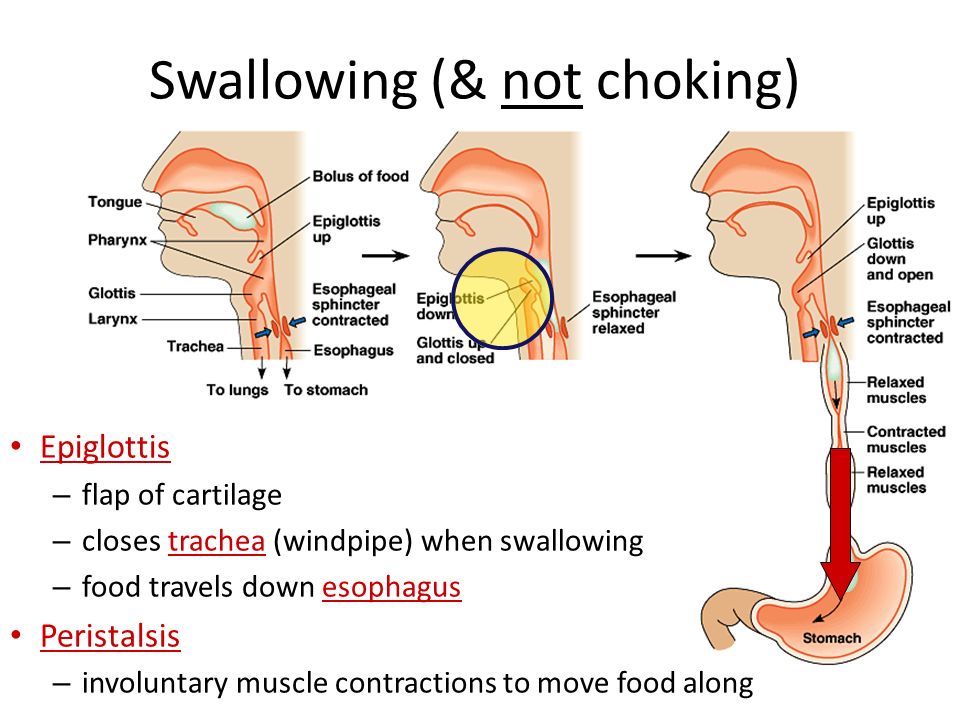
Definition
Choking is a form of suffocation/asphyxia due to obstruction of the respiratory airway. It is caused by inhalation and/or ingestion of a foreign object that partially or completely blocks the airway, the entrance to the trachea – respiratory passage – usually between pharynx and bifurcation of trachea.
Description
Choking is a very dangerous life threatening medical situation which leads to respiratory suffocation and if not addressed “promptly and appropriately” in cardiac arrest.
Partial Airway Obstruction: If airway obstruction is partial, the victim if not panicked, especially if it is an adult, can cough and expel the foreign object without assistance and/or medical care.
Complete Airway Obstruction: If airway obstruction is complete, usually occurs when a foreign object is inhaled and becomes stuck (like a cork) between the vocal cords, and regardless of the age of the victim, particularly in case of children and elderly people, removal of the foreign object is impossible without assistance and/or medical care, leading the victim not to be able to breathe.
Breathing is an essential part of life. When we inhale, we breathe in a mix of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases.
In the lungs, oxygen enters the bloodstream to travel to the rest of the body. Our bodies use oxygen as a fuel source to make energy from the food we eat. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, enters the bloodstream and travels back to the lungs.
When we exhale, we breathe out carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and oxygen. When someone is choking with a completely blocked airway, no oxygen can enter the lungs.
In this case Choking requires fast, appropriate action by anyone available. The brain is extremely sensitive to this lack of oxygen and begins to die within four to six minutes. It is during this time that first aid must take place. Irreversible brain death occurs in as little as 10 minutes.
Emergency medical teams may not arrive in time to save a choking person’s life.
We all are!
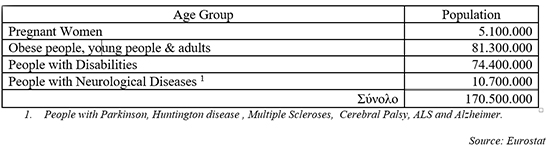
Although the majority of choking occurs in the very young and the elderly, no one is totally immune, not even healthy young adults.
Swallowing is a complex action that most of us take for granted. A sudden gasp and a foreign object can be inhaled. Nothing is for granted!
These facts are proven and recorded by many independent international organizations and agencies all over the planet.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Choking is one of the five leading causes of unintentional injury death.
Particularly in the European Union data show that:
- 60% of the cases in children are caused by food related hazards, with the respective figure for adults to be around 85%.
- 30% of the cases in children are caused by non-food related hazards like plastic and small metal parts, coins and toys, with the respective figure for adults to be around 10%.
- 10% of the cases in children are caused by other causes, with the respective figure for adults to be around 5%.
So every year it is estimated that around:
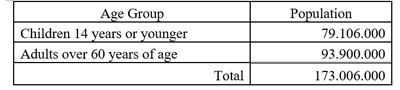
- 400 children (14 years or younger) die from choking.
- 50.000 children (14 years or younger) have a choking episode.
- 3.000 adults die from choking on food.
- 280.000 adults have a choking episode.
High Risk Population in European Union:
Age Groups:
Sensitive Age Groups:
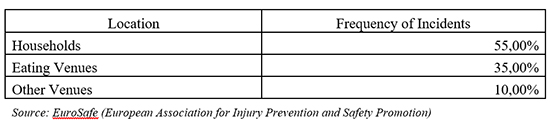
High Risk Worldwide Locations:
American Pediatric Academy, after a scientific research published in 2010 has recognized that the following food and items pose a high risk hazard and can lead to Choking:
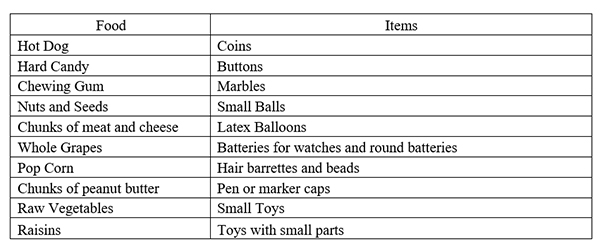
Especially for Hot Dog, in the same report, there was an extend notification as 17% of the Choking cases, for children under the age of 10, were caused from Hot Dog. As it is reported the shape and the diameter of a Hot Dog has the same shape and diameter of a child’s upper airway resulting, if not eaten correctly, to form a plug, completely sealing off the upper airway, right above the vocal chords!!!
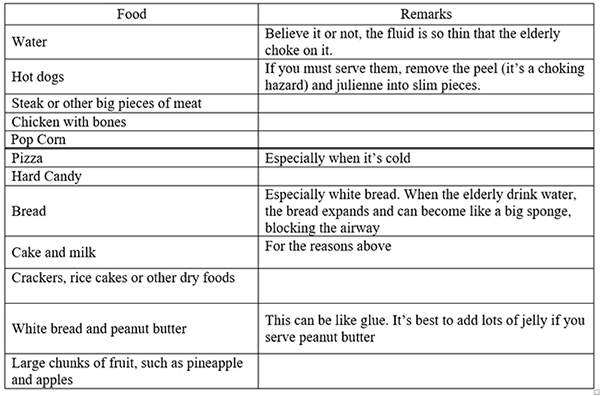
At the same time C.D.C. the American Center for Disease Control and Prevention published a report concerning the elders and especially those over 60 years of age, according to which the most serious hazards of Choking are:
For Children: Keep children away from items and food that are mentioned above in order to avoid a Choking incident. Also:
- Supervise children while eating and playing
- Create a safe environment for playing by removing all small toys and items
- Cut food into very small pieces
- Monitor older children to be sure that they don’t give to the younger food or other items
- Educate children to sit in the upright position while eating
- Learn CPR and the Heimlich maneuver
For the elderly and the rest vulnerable population groups: Concerning food choose those that are easier to swallow such as filleted fish, ground meat, soups, chocolate, (if it gets stuck, it melts), applesauce, pudding and jell-o, lightly toasted bread with butter or jelly. Also:
- If you serve apples make sure that they are peeled
- Create a calm environment in order of slow consumption of food
- Don’t allow food to be consumed while a person is walking or running with speed
- Learn CPR and the Heimlich maneuver
Whatever prevention measures we take risk never stops to exist it’s only limited by the extent of the actions taken, this as we all know is the basic principle of risk management.
Actions taken on a Choking Incident when the obstruction of the airway is complete and the victim cannot breath: Call 112 (international emergency number) and then use LifeVac immediately.
Why?
Because: a victim due to oxygen lack:
- In 0-4 min, it’s unlikely to suffer Brain Damage
- In 4-6 min, it’s possible to suffer Brain Damage
- In 6-10 min, it’s almost certain to suffer Brain Damage
- In 10+ min, without oxygen, victim will be Brain Dead
- Notice: Average response time of EMS: min 10 min
And as the minutes pass and the victim cannot breathe, it faints from lack of oxygen resulting to Cardiac Arrest.